Time to introduce you to Chapter V of EDU MAP’s reference handbook for substance abuse. It investigates short and long term effects of substance abuse.
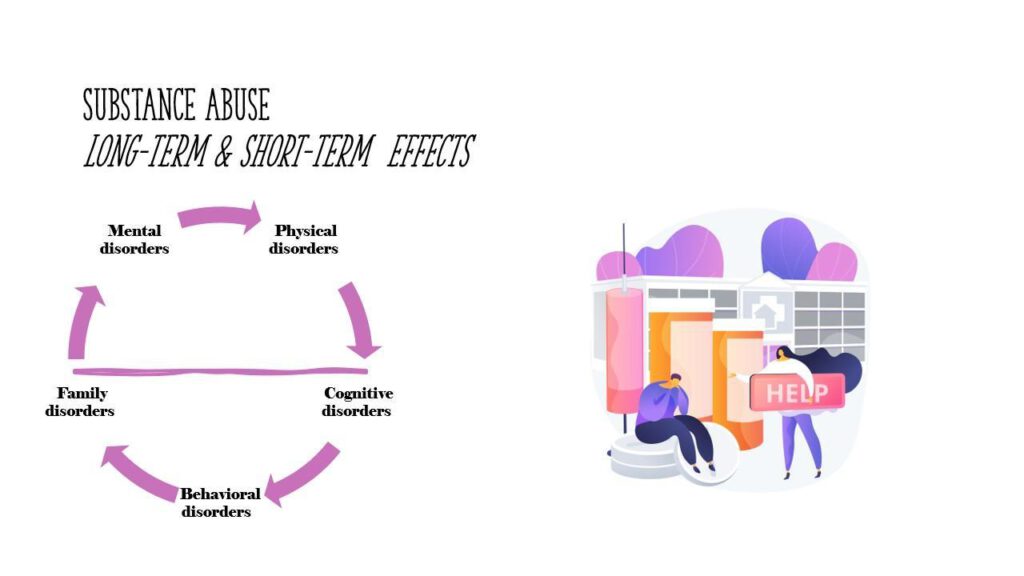
Substance abuse may provoke multiple repercussions, affecting the physical, mental, and behavioral wellbeing of users. The use of drugs, alcohol, or any other toxic substance for a prolonged period of time may transform a short-term effect into a long-term one, while the possibility of death is not excluded from the list of the effects that may occur. The continuous use of substances is responsible for causing crucial implications to the users that may not be rehabilitated again.
As far as the implications to the youth are concerned, the use of illicit substances is related to phenomena like tendency to dropping out, social exclusion, dissolution of the structure of the family, illegal activity and crime, as well as illiteracy. These factors contribute to the mental instability, which may be expressed in different ways, including suicide.
As far as the physical implications are concerned, there are numerous diseases and disorders that are caused by the addiction to substances, such as pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary edema, aspiration pneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, tuberculosis, Hepatitis B, C and D, acute and chronic kidney injury, interstitial nephritis, and glomerulonephritis. Disorder in organ functions, blood pressure and heart rate, as well as effects on the appearance of the body constitute some of the negative health effects of substance use.
Last but not least, there are several behavioral and cognitive effects that are caused by substance abuse, among them, assertive behavior, physical abuse, chronic anxiety, and decision-making disorders.
To sum up, both the short- and long-term effects that may be provoked because of substance abuse are perilous and dangerous to humans, and may constitute a direct threat to life.









